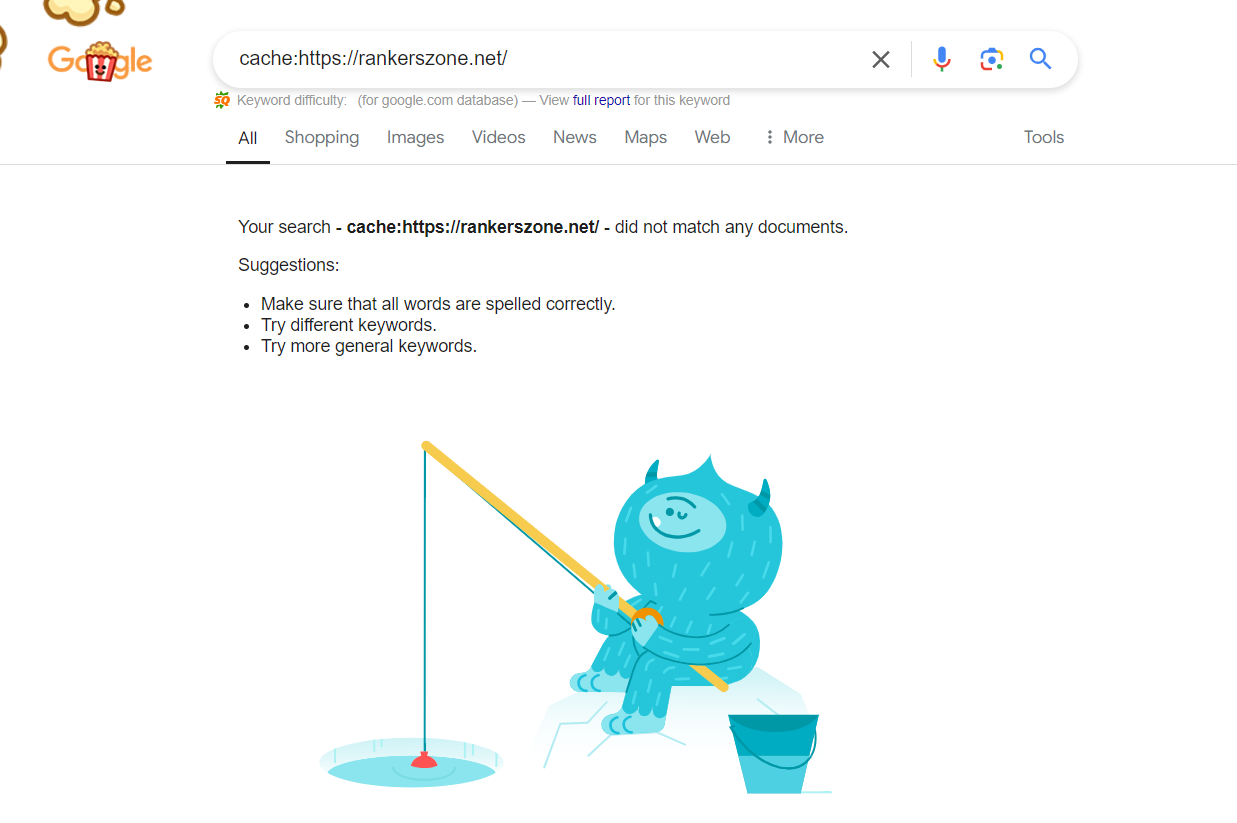
The Google cache operator, a key tool for accessing old web pages, is no longer available. This change affects many, including website owners, webmasters, and researchers. They used it for SEO analysis and saving content.
The Google cache operator let users see a web page’s snapshot from Google’s cache. It was a favorite for many in the digital world. But, Google has stopped this feature, leaving many wondering about its impact on their online work and research.
Key Takeaways
- Google has discontinued the cache operator, a feature that allowed users to access cached versions of web pages.
- This change impacts website owners, webmasters, and researchers who relied on the cache operator for various purposes, such as SEO analysis and content preservation.
- Alternative solutions, such as third-party cache services and the Internet Archive’s Wayback Machine, are available to access cached content.
- Optimizing website performance and mobile-friendliness is crucial in the wake of this change to maintain a strong online presence.
- Understanding the reasons behind the cache operator’s discontinuation and adapting to the new landscape are essential for navigating this shift in the digital ecosystem.
Unveiling the Demise of Google’s Cache Operator
The google cache operator was a key feature. It let users see how web pages looked when Google indexed them. It was a favorite among website owners, SEO experts, and researchers. They used it to check for changes, find broken links, and study past data. But, Google has slowly stopped supporting this feature, leaving many wondering why.
Understanding the Cache Operator’s Purpose
The google cache was essential for how people used the google search engine. It gave users a snapshot of a web page, even if it was gone or changed. This was super helpful for fixing problems, doing research, and keeping up with the web.
Reasons Behind the Discontinuation
Even though the cache feature was loved, Google decided to phase it out. Several reasons led to this choice, including:
- Changes in how people use the internet and the rise of live updates
- Worries about the misuse of the cache operator for bad purposes
- New tech that made web caching better and more common, making the cache operator less needed
As Google keeps improving its search engine and focusing on user needs, the google cache operator is no longer as important. This has led to its slow decline.
Impact on Website Owners and Webmasters
The end of the Google cache operator has changed things for website owners and webmasters. They can’t easily check past versions of web pages anymore. This makes it tough to keep track of changes, find broken links, and see how websites have done in the past.
Website owners and webmasters can’t see past versions of their pages like they used to. This makes it harder to find and fix problems like broken links or old information. These issues can hurt how well a website works and its ranking on search engines.
SEO experts also face challenges without the Google cache operator. They can’t quickly look at past versions of web pages. This means they have to find new ways to do their work, which takes more time and effort.
| Impact | Challenges for Website Owners and Webmasters | Challenges for SEO Professionals |
|---|---|---|
| Content Monitoring | Harder to track changes to web page content | Difficulty in monitoring content updates and revisions |
| Link Tracking | More difficult to identify and fix broken links | Decreased ability to audit link integrity across web pages |
| Performance Analysis | Limited access to historical website performance data | Reduced capability to analyze website performance over time |
| Content Auditing | Challenges in conducting comprehensive content reviews | Hindered ability to perform thorough content audits |
The loss of the Google cache operator has brought new hurdles for website owners, webmasters, and SEO experts. They must now find new ways to keep up with web page changes, analysis, and content optimization. This is a big change from what was possible with the cache operator.
Alternative Solutions for Accessing Cached Pages
Even though the Google cache operator is gone, there are still ways to see old web pages. These new services help us look at old content and keep important info safe.
- Cole Hocker: The Rising Star of Middle-Distance Running
- Ryan Crouser: The Shot Put Sensation Redefining the Sport
- Caroline Marks: Surfing’s Rising Star
- Emma Weyant: The Quiet Storm of Swimming
- what are backlinks in seo?
Utilizing Third-Party Cache Services
Third-party services like Bing’s Cached Pages and DuckDuckGo’s !cache command are good options. They keep their own copies of web pages. This lets users see cached web pages when the original site is down.
Leveraging the Internet Archive’s Wayback Machine
The Internet Archive’s Wayback Machine is also a great tool. It’s a big archive of web pages that lets you see old versions of sites. It’s perfect for researchers, historians, and anyone looking for alternative cache services.
| Service | Description | Advantages |
|---|---|---|
| Bing Cached Pages | Bing’s built-in cache of web pages | Provides access to cached content, especially when the original source is unavailable |
| DuckDuckGo !cache | DuckDuckGo’s command to view cached versions of web pages | Allows users to quickly access cached web pages directly from the search engine |
| Internet Archive Wayback Machine | Comprehensive archive of web pages over time | Offers a wealth of historical web page history and content preservation for research and reference purposes |
With these alternatives, users can still find and explore cached web pages without the Google cache operator. These alternative cache services and the Internet Archive are key for keeping and accessing online content.
google cache operator dead
The Google cache operator, once a key tool, is no longer available. This change shows how search engine tech is always changing. Now, users must find new ways to see old web pages.
This tool let users see old versions of web pages. It was useful for checking content and doing historical research. But Google has stopped supporting it, leaving many looking for new options.
Implications of the Cache Operator’s Discontinuation
Without the cache operator, many are facing big changes. Website owners can’t quickly check if their content is working right. Researchers also lost a key tool for studying web page changes.
This change shows search engines now focus on fresh, up-to-date info. They don’t keep big archives of old web pages anymore.
Adapting to the New Landscape
Now, users need to find other ways to see old web pages. Services like the Wayback Machine and third-party caches are good options. But they might not work the same way.
Website owners and webmasters need to make their sites better for search engines. This means making sites mobile-friendly, fast, and easy to find. They should use other search engine tools to keep their content visible.
The end of the Google cache operator is a big change in the search world. It brings challenges, but also shows the need to stay flexible with digital tech. As things keep changing, website owners and webmasters must find new ways to make their content easy to find.
Optimizing Your Website for Search Engines
With Google’s cache operator gone, website owners need new strategies. They must focus on making their sites mobile-friendly and fast. This helps them stay ahead in the changing search engine world.
Embracing Mobile-Friendly Design
More people use mobile devices to surf the web. So, it’s key to make sure your site works well on phones. Using responsive design is essential. It makes your site look good on any screen size, keeping users happy and search engines ranking you high.
Enhancing Site Speed and Performance
Site speed is also crucial. Slow sites can lose users and hurt your search rankings. To speed up your site, try optimizing images, minifying code, and using a content delivery network (CDN). These steps make your site faster and more user-friendly, boosting your search engine ranking.
FAQ
What was the Google cache operator?
The Google cache operator was a tool that showed web pages as they were when Google indexed them. It was used by many to track changes, find broken links, and study past data.
Why was the Google cache operator discontinued?
Google stopped using the cache operator as search technology evolved. Now, they focus more on showing the latest content.
What impact does the discontinuation of the Google cache operator have on website owners and webmasters?
Without the Google cache operator, it’s harder for website owners and webmasters to keep track of changes. They can’t easily find broken links or analyze past website performance. SEO experts also face challenges in doing detailed content audits.
What are some alternative solutions for accessing cached web pages?
Even though the Google cache operator is gone, there are other ways to see cached web pages. Services like Bing’s Cached Pages and DuckDuckGo’s !cache command can help. The Internet Archive’s Wayback Machine also offers a vast archive of web pages for historical views.
How can website owners and webmasters optimize their websites for search engines in the absence of the Google cache operator?
Without the Google cache operator, website owners and webmasters need to use other strategies. They should make their sites mobile-friendly, improve site speed, and follow best practices for content. These steps can help them stay visible in search engines and provide a better user experience.